Progeria is a rare genetic condition that causes a person to age prematurely. Children with progeria appear healthy, but by the age of 2 years, they look as if they have become old too fast.single mistake in a certain gene causes it to make an abnormal protein. A single mistake in a certain gene causes it to make an abnormal protein , When cells use this protein, called progerin, they break down more easily. Progerin builds up in many cells of kids with progeria, causing them to grow old quickly. Progeria is not inherited, or passed down in families.

• SYMPTOMS :-
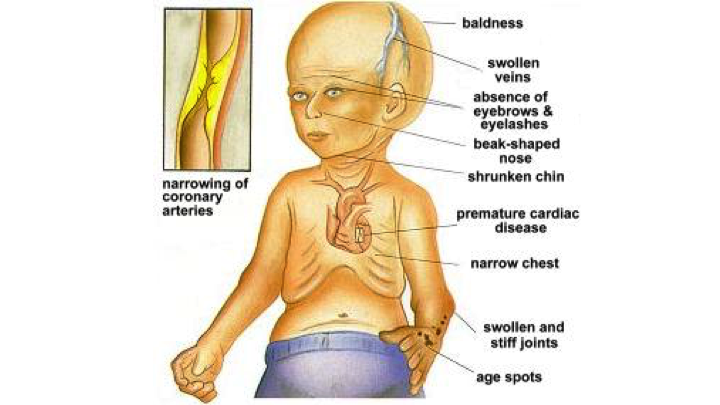
Most kids with progeria look healthy when they're born, but they start to show signs of the disease during their first year. They develop physical traits including:
- A bigger head
- Large eyes
- A small lower jaw
- A thin nose with a "beaked" tip
- Ears that stick out
- Veins you can see
- Slow and abnormal tooth growth
- A high-pitched voice
- Loss of body fat and muscle
- Hair loss, including eyelashes and eyebrows
• CAUSES :-
A single gene mutation is responsible for progeria. The gene, known as lamin A (LMNA), makes a protein necessary for holding the center (nucleus) of a cell together. When this gene has a defect (mutation), an abnormal form of the lamin A protein called progerin is produced and makes cells unstable. This appears to lead to progeria's aging process.
Unlike many genetic mutations, progeria is rarely passed down in families. The gene mutation is a rare, chance occurrence in the majority of cases.
• TREATMENT :-
There's no cure for progeria, but regular monitoring for heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease may help.
During medical visits, your child's weight and height is measured and plotted on a chart of normal growth values. Additional regular evaluations, including electrocardiograms and dental, vision and hearing exams, may be recommended by your doctor to check for changes.
Certain therapies may ease or delay some of the signs and symptoms. Treatments depend on your child's condition and symptoms.
These may include:
- Low-dose aspirin. A daily dose may help prevent heart attacks and stroke.
- Other medications. Depending on your child's condition, the doctor may prescribe other medications, such as statins to lower cholesterol, drugs to lower blood pressure, anticoagulants to help prevent blood clots.
- Physical and occupational therapy. These therapies may help with joint stiffness and hip problems .
- Nutrition. Nutritious, high-calorie foods and supplements can help maintain adequate nutrition.
- Dental care. Dental problems are common in progeria. Consultation with a pediatric dentist.
<3
ReplyDelete