Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes hyperthyroidism, or overactive thyroid. With this disease, your immune system attacks the thyroid and causes it to make more thyroid hormone than your body needs.An immune system disorder of the butterfly-shaped gland in the throat (thyroid). Because thyroid hormones affect a number of different body systems, signs and symptoms associated with Graves' disease can be wide ranging and significantly influence your overall well-being. Although Graves' disease may affect anyone, it's more common among women and before the age of 40, than in man.
• SYMPTOMS :-
Common signs and symptoms of Graves' disease include:
- Anxiety and irritability
- A fine tremor of your hands or fingers
- Thick, red skin usually on the shins or tops of the feet
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Frequent bowel movements
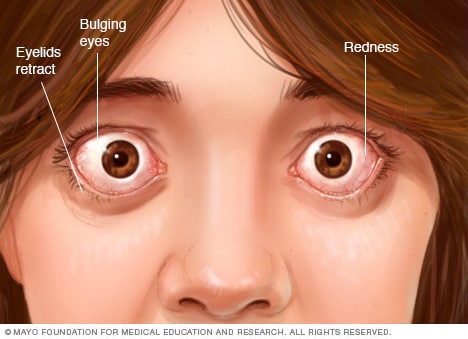
- Bulging eyes
- Fatigue
- Enlargement of your thyroid gland (goiter)
- Change in menstrual cycles
- Erectile dysfunction or reduced libido
• CAUSES :-
Graves' disease is caused by a malfunction in the body's disease-fighting immune system, although the exact reason why this happens is still unknown. In Graves' disease — for reasons that aren't well understood — the body produces an antibody to one part of the cells in the thyroid gland, a hormone-producing gland in the neck. Basically thyroid function is regulated by a hormone released by a tiny gland at the base of the brain (pituitary gland). The antibody associated with Graves' disease — thyrotropin receptor antibody (TRAb) — acts like the regulatory pituitary hormone. That means that TRAb overrides the normal regulation of the thyroid, causing an overproduction of thyroid hormones.
Graves' ophthalmopathy often appears at the same time as hyperthyroidism.
This condition results from a buildup of certain carbohydrates in the muscles and tissues behind the eyes — the cause of which also isn't known.
- Family history. Because a family history of Graves' disease is a known risk factor, there is likely a gene or genes that can make a person more susceptible to the disorder.
- Gender. Women are much more likely to develop Graves' disease than are men.
- Age. Graves' disease usually develops in people younger than 40.
- Other autoimmune disorders. People with other disorders of the immune system, such as type 1 diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, have an increased risk.
- Emotional or physical stress. Stressful life events or illness may act as a trigger for the onset of Graves' disease among people who are genetically susceptible.
- Pregnancy. Pregnancy or recent childbirth may increase the risk of the disorder, particularly among women who are genetically susceptible.
- Smoking. Cigarette smoking, which can affect the immune system, increases the risk of Graves' disease. Smokers who have Graves' disease are also at increased risk of developing Graves' ophthalmopathy.
• TREATMENT :-
1.Anti-thyroid medication
2.Radioactive iodine therapy.
3. Surgery.
4. Beta Blockers.
• Foods to Eat More of If You Have Graves’ Disease :-
1. Berries.
2.Milk products.
3. Food with vitamin D
4. Green vegetables.
5. Protein.
6.Omega 3
• What to Limit When You Have Graves' Disease :-
1. Caffeine
2. Oily food
3. Food allergens.
Comments
Post a Comment